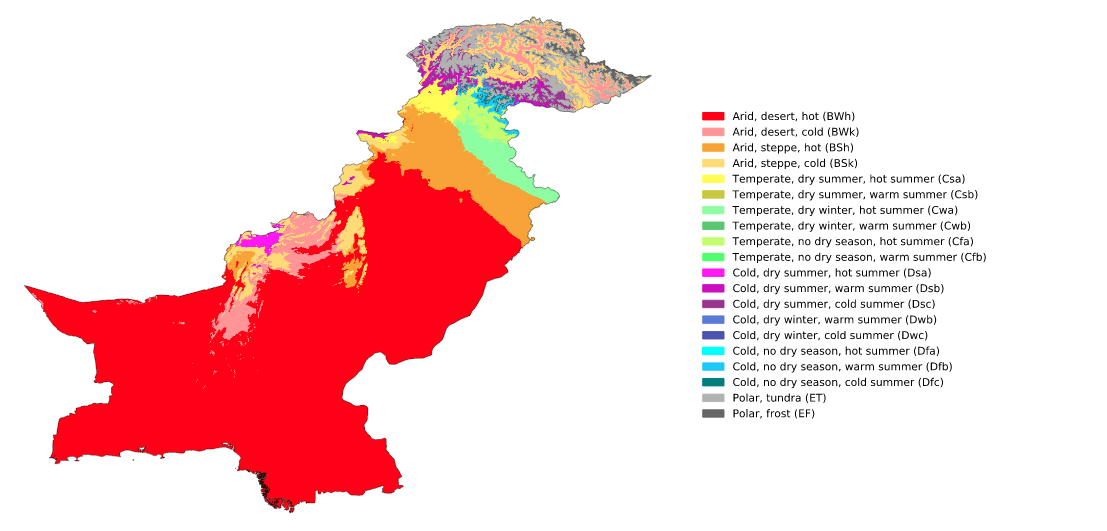
Pakistan lies on the western margin of one of the major climatic regions the monsoon region. The climate of Pakistanis more Continental than of other parts of the subcontinent, which comes under a more typical monsoon regime.
Climate is a composite term and refers to a number of elements, including temperature, air pressure, wind, rainfall and Snowfall etc. These elements also act as climatic factors. Climate is an impotent subject of scientific enquiry, particularly as it has such an impact on vegetation and soil.
Its importance to any economy and especially that of Pakistanis greatly influenced by climate because it determines the type of crop grown in particular regions and the need, if any for irrigation. Natural hazards like Storms, floods and desertification are the result of climate changes. Extreme temperature, whether hot are cold, affect human beings, crop and animals. Solar energy and wind are used to generate electricity. In short, there are many ways in which climate affects our daily lives.
In winter, due to reversal of wind system climatic conditions are quite different in this season, they prevail from north-west to southwest from land to sea. In winter rainfall is quite insufficient and its usefulness for agriculture is further reduced by its variable nature.
Due to limited monsoon rainfall, a major part of Pakistan is dominated by dry climate, only a small area in north experiences humid sub-tropical climate. In the extreme north, because of great heights highland climate prevails.
Conspicuousness and diversity are the two notable physiographic features of Pakistan, it occupies the western end of the indo-Genetic plain, which is bounded the north by mountain wall of Great Himalaya sand their off shoots. These physical features have a great bearing on the climatology of the area in so much as they not only modify rainfall and temperature pattern of Pakistan but also influence the general circulation of the atmosphere in the subcontinent. The climate of a particular place is determined by several factors, including latitude, coastal and continental location, prevailing winds and altitude. Therefore, like rest of the subcontinent, Pakistan has four seasons. These may be distinguished as follows:
Cold Weather Season – December to March
Hot Weather Season – April to June